In addition to being a pressing public health emergency both in Türkiye and across the World, COVID-19 is a phenomenon that has an impact on the economy, social relations, and daily routines. Getting such a pandemic under control requires not only concerted efforts from both health organizations and governments but also that individuals take measures to reduce their exposure to the disease. As such, it is imperative that individuals have sufficient access to health information and adhere to recommended safety measures to stem the contagion.
At a time when “knowledge” about COVID-19 is quickly evolving, mass communication media (newspapers, television, internet, and social media) have a crucial role in terms of the overall health of the information environment. Mainly, but not solely, social media, while providing added benefits to help people maintain their connections, are prone to spread false information, claims thatare yet to be scientifically substantiated, and even recommendations that may expose individuals to health risks.
Funded by the TUBITAK ARDEB 1001- Scientific and Technological Research Projects Funding Program (COVID-19 and Society: Social, Human and Economic Effects of the Outbreak, Problems and Solutions), this project aims to investigate information disseminated on mass media and social media as factors that may influence COVID-19 risk perceptions and the extent to which individuals adopt health-protective behaviors or behaviors that may put them at risk concerning COVID-19. The project brings together researchers from Koç University (PI), Duke University, and the National University of Singapore.
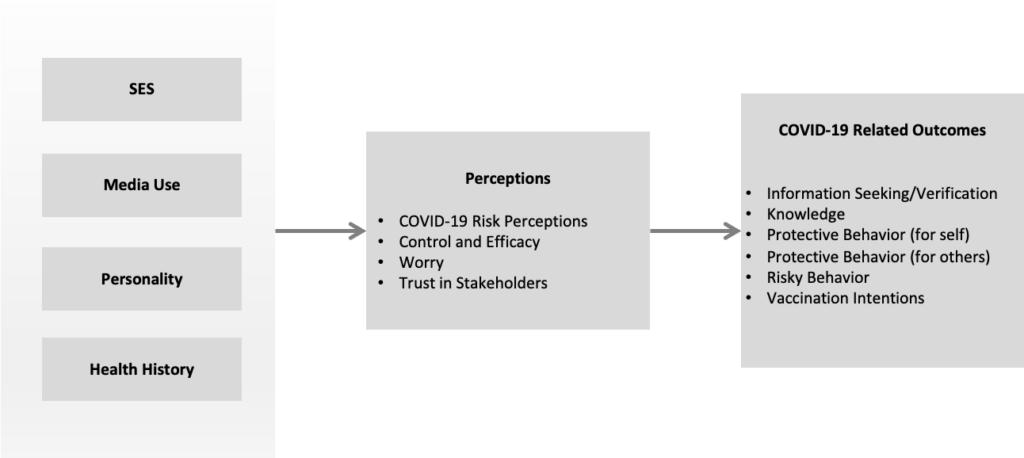
The project has three main components: 1) Application of machine learning techniques for analysis of content about COVID-19 on social media (Twitter), 2) A content analysis of news about COVID-19 published by national newspapers, and 3) An online survey, along with modules containing survey-experiments.


